Xanthan gum is a versatile food additive that has gained popularity in the food industry for its unique properties and wide range of applications. It is a polysaccharide, meaning it is a long-chain carbohydrate composed of sugar molecules. Xanthan gum is produced through the fermentation of sugars, typically derived from sources such as corn, soy, or wheat, by the Xanthomonas campestris bacterium. This fermentation process results in the formation of a gel-like substance, which is then dried and ground into a fine powder to produce xanthan gum.
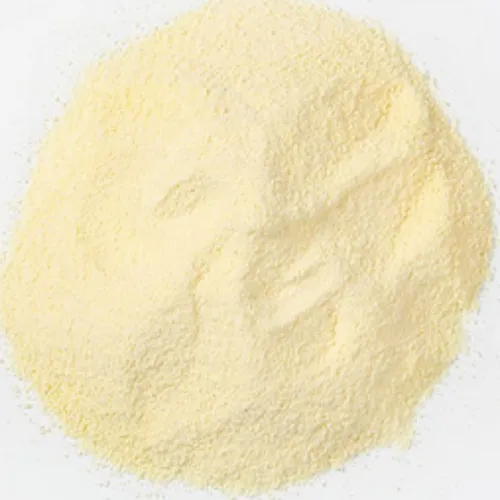

The discovery of xanthan gum dates back to the early 1960s when scientists at the U.S. Department of Agriculture were conducting research on microbial polysaccharides. The bacterium Xanthomonas campestris was found to produce a viscous substance when it consumed sugars. This substance was identified as xanthan gum and later found to possess several remarkable properties, making it an invaluable ingredient in the food and other industries.
Xanthan Gum is a hydrocolloid, meaning it can interact with water and form a gel-like structure. It is a high molecular weight polysaccharide, composed of repeated units of glucose, mannose, and glucuronic acid. The specific composition and arrangement of these sugar units give xanthan gum its unique properties, including its thickening, stabilizing, emulsifying, and suspending capabilities.
One of the most prominent features of xanthan gum is its remarkable viscosity, even at low concentrations. When added to water or other liquids, xanthan gum rapidly disperses and hydrates, forming a highly viscous and pseudoplastic solution. Pseudoplasticity means that the substance behaves like a solid under static conditions but flows like a liquid when subjected to shear or force. This property allows xanthan gum to thicken and stabilize a wide range of food products, including sauces, dressings, dairy products, and bakery fillings, without affecting their texture or appearance.
Xanthan gum is also an effective emulsifier, helping to create and stabilize emulsions, which are mixtures of immiscible liquids like oil and water. In salad dressings, for example, xanthan gum can help prevent the separation of oil and water phases, ensuring a smooth and consistent texture.
Another valuable characteristic of xanthan gum is its ability to suspend particles in liquids. In beverages with added pulp or particles, xanthan gum helps keep the particles evenly distributed throughout the liquid, preventing settling or separation.
Beyond its applications in the food industry, xanthan gum is utilized in various other sectors, such as pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and industrial processes. In pharmaceuticals, it can act as a binder or thickener in liquid medications, while in personal care products like toothpaste and lotions, it provides texture and stability.
The safety of xanthan gum as a food additive has been extensively studied and approved by regulatory authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). It is generally considered safe for consumption by the general population, including those with celiac disease, as it is gluten-free. However, like any food ingredient, some individuals may be sensitive to xanthan gum and experience gastrointestinal discomfort when consuming large quantities.

In conclusion, xanthan gum is a valuable food additive derived from the fermentation of sugars by the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris. Its exceptional thickening, stabilizing, emulsifying, and suspending properties make it a widely used and trusted ingredient in the food industry and various other applications. As with any food additive, it is essential to use xanthan gum in appropriate amounts and follow regulatory guidelines to ensure the safety and quality of the final products.

 English
English
 Español
Español
 Português
Português
 русский
русский
 français
français
 日本語
日本語
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
 Italiano
Italiano
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 ไทย
ไทย
 Polski
Polski
 한국어
한국어
 Svenska
Svenska
 magyar
magyar
 Malay
Malay
 বাংলা
বাংলা
 Dansk
Dansk
 Suomi
Suomi
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी
 Pilipino
Pilipino
 Türk
Türk
 Gaeilge
Gaeilge
 عربى
عربى
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 norsk
norsk
 اردو
اردو
 čeština
čeština
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά
 Українська
Українська
 فارسی
فارسی
 नेपाली
नेपाली
 Burmese
Burmese
 ລາວ
ລາວ
 Latine
Latine
 Қазақ
Қазақ
 Македонски
Македонски
 Lietuvos
Lietuvos
 Română
Română
 मराठी
मराठी
 Српски
Српски
 Esperanto
Esperanto
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
 Беларус
Беларус
 Hrvatski
Hrvatski
 Hausa
Hausa
 Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл
 Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig
 O'zbek
O'zbek






